Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport Luchthaven Brussel Aéroport de Bruxelles | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public / military | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Brussels Airport Company | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | |||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Zaventem, Flemish Brabant, Belgium | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for | TUI fly Belgium | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 184 ft / 56 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 50°54′05″N 004°29′04″E / 50.90139°N 4.48444°E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||
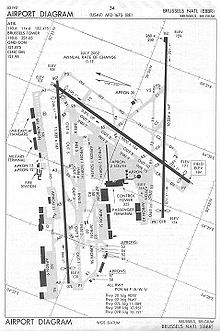 Airport diagram | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2019) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Brussels Airport (Dutch: Luchthaven Brussel, French: Aéroport de Bruxelles) (IATA: BRU, ICAO: EBBR) is the main international airport of Belgium. It is located in the municipality of Zaventem in Flemish Brabant, 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) northeast[2] of Brussels.
Also informally known as Brussels-National Airport (Luchthaven Brussel-Nationaal, Aéroport de Bruxelles-National) or Brussels-Zaventem Airport (Luchthaven Brussel-Zaventem, Aéroport de Bruxelles-Zaventem), Brussels Airport handled more than 26 million passengers in 2019, making it the 26th busiest airport in Europe. It is home to around 260 companies, together directly employing 20,000 people and serves as the home base for Brussels Airlines and TUI fly Belgium. BRU covers 1,245 hectares (3,076 acres) and contains three runways.[3]
The company operating the airport is known as The Brussels Airport Company N.V./S.A.; before 19 October 2006, the name was BIAC (Brussels International Airport Company), which was created by Belgian law through a merger of BATC with the ground operations departments of the RLW/RVA. Since 2011, the airport has been owned by the Toronto-based Ontario Teachers' Pension Plan (39%), Macquarie Group (Macquarie European Infrastructure Fund I and Macquarie European Infrastructure Fund III) (36%) and the Belgian State (25%).[4]
On 22 March 2016, the airport's departures hall was severely damaged by two terrorist bomb blasts. The airport was closed until 3 April 2016, when it was reopened with temporary facilities at less than 20% of its previous capacity.[5] It has since returned to full operations, with a record of 90,000 passengers on 29 July 2016.[6]
History
[edit]Early years
[edit]The origins of Brussels Airport at Zaventem date back to 1940, when the German occupying force claimed 600 ha (1,500 acres) of agricultural fields reserved as a back-up airfield ("Steenokkerzeel"). There the Luftwaffe established Fliegerhorst Melsbroek and constructed three runways in the shape of a triangle: runway 02/20, runway 07L/25R (both of which are still in use today) and runway 12/30. The airport buildings were constructed in the nearby municipality of Melsbroek and not of Zaventem, which is why the airfield was known to the locals as Melsbroek (in Dutch) (or "Fliegerhorst Melsbroek" in German). There is an urban legend that the site of the airport was chosen by the Germans after asking locals where to build it–the Belgians then pointed to this location as it was often foggy.[citation needed]

After the liberation on 3 September 1944, the German infrastructure at Melsbroek fell into the hands of the British. When the old civilian airport in Haren became too small, the Belgian authorities decided to use the aerodrome at Melsbroek for the new national airport. By 1948, a new terminal building was constructed to replace the old wooden building. In the same year, the lengths of both runways 02/20 and 07L/25R were increased, to 1,200 m (3,900 ft) and 2,450 m (8,040 ft) respectively, whereas 12/30 remained at 1,300 m (4,300 ft). The civil aerodrome of Melsbroek was officially opened by Prince Charles, Count of Flanders, the prince regent, on 20 July 1948. From 1948 to 1956, many more buildings and facilities were erected, mostly on the Melsbroek side of the site.[citation needed]
In 1955, a railway line from Brussels city centre to the airport was constructed. The line was officially opened by King Baudouin on 15 May 1955.[citation needed]
In 1956, a new 2,300 m (7,500 ft) runway was constructed, 07R/25L, which almost runs parallel with 07L/25R. The runway is still in use today and saw its length later increased to 3,200 m (10,500 ft). In April 1956, the Belgian government decided to build a new airport, using the same runways, but with the buildings located within the municipality of Zaventem. In April 1957, construction started of the new terminal, preparing the airport for the 1958 World's Fair (Expo 58). The grass runway 12/30 had to make way to allow for the new passenger terminal. This new airport was inaugurated on 5 July 1958, just in time for the 1958 World’s Fair. The buildings on the Melsbroek side are still in use by the Belgian Air Force (15th Air Transport Wing), and this is still known as Melsbroek Airfield. Both Zaventem Airport and Melsbroek Air Base, the military airfield, share the same runways.[7][8]
Development since the 1960s
[edit]

During the boom of commercial aviation in the 1960s and 1970s, several hangars were constructed. A new cargo terminal was constructed in 1976. In 1994, a brand new terminal was constructed adjacent to the old 1958 building. Two old piers were torn down and replaced by modern ones. In 2002, amidst the turmoil surrounding the demise of the national airline Sabena, a new pier was opened.
In 2005, the airport was awarded Best Airport in Europe by Airports Council International / International Air Transport Association (ACI/IATA), based on a survey of over 100,000 passengers worldwide. Brussels Airport continued to appear in top airports lists as of 2012. A direct train link with Leuven and Liège was opened on 12 December 2005.
In 2007, the airport served 17.8 million passengers, an increase of 7% over 2006. The cargo volume in the same year amounted to 780,000 tonnes, an increase of 8.9% over 2006. In 2008, the airport served 18.5 million passengers, which was an increase of 3.7% over the previous year.[9]
Sabena's demise meant a sharp fall in passenger traffic, a blow from which the airport only slowly recovered. The airport's future is threatened by disagreement between the governments of Flanders and the Brussels Capital Region concerning night-time air traffic routes.
In March 2009, the old mechanical Flight information display systems were replaced by electronic ones.[10] In September 2009, CEO Wilfried Van Assche resigned. One of the (unofficial) reasons was the delay in the construction of the low-cost terminal and the possible lawsuit by 52 airlines active at Brussels Airport, on the grounds of tax discrimination. It was Van Assche who started expanding the Long-Haul network (Jet Airways, Hainan Airlines, Etihad Airways and US Airways) at Brussels Airport. In February 2010 Arnaud Feist was appointed CEO. The Chairman of the Board is Marc Descheemaecker.
- On 18 February 2013, in the 2013 Belgium diamond heist, eight men armed with automatic weapons and dressed in police uniforms seized 120 small parcels containing an estimated US$50 million worth of diamonds from a Helvetic Airways Fokker 100 passenger plane loaded with passengers preparing for departure to Zürich. The men drove two vehicles through a hole they had cut in the airport perimeter fence to Flight LX789, which had just been loaded with diamonds from a Brink's armored van from Antwerp. They carried out the operation within five minutes with no injuries and without firing a shot.[11][12][13]
2016 Brussels bombings
[edit]On 22 March 2016, two explosions took place in Brussels Airport at 07:58 local time. One occurred near the American Airlines and Brussels Airlines check-in desks and the other next to a Starbucks coffee shop. A third bomb was found in the airport and detonated in a controlled explosion. The airport was closed after the attacks until 3 April, when it reopened with temporary facilities at less than 20% of its previous passenger capacity.[5] Flights bound to Brussels Airport were either canceled or diverted to nearby airports such as Brussels South Charleroi Airport, Ostend–Bruges International Airport, and Schiphol. At 09:11 CET, an explosion took place at Maelbeek/Maalbeek metro station. ISIL claimed responsibility for the attacks as an act of revenge against Belgium for participation in the ongoing Military intervention against ISIL.[14]
Facilities
[edit]



Brussels Airport uses a one terminal concept, meaning that all the facilities are located under a single roof. The terminal building consists of several levels. The railway station is located on −1, buses and taxis arrive at 0, arrivals are located on level 2 and departures on level 3. Levels 2 and 3 are connected to the airport's two piers (A and B).[15]
Pier A
[edit]The newest pier in Brussels airport was pier A, opened on 15 May 2002. This pier was destined to support flights from and to the Schengen countries (A-gates). However, since 15 October 2008 all Brussels Airlines flights to African destinations are also handled at this pier. Therefore, border control was installed towards the end of the pier in order to create a new pier. As a result, gates A61-72 were renamed T61-72. Later, Brussels Airlines' daily flight to New York was also moved here from pier B.
Until 26 March 2015,[16] Pier A was connected to the main building via a 400-metre-long (1,300 ft) tunnel under the apron. Each pier used to have its own security zone, so transfer between the piers involved a security check, which for practical purposes made it to be two terminals. This tunnel was replaced by the "Connector", a new building that links both piers above ground and allows passengers to walk straight from the check-in desk to their gate in pier A or B, without changing floors. In the opposite direction, the building provides arriving passengers with a smooth and convenient passage to the baggage reclaim hall and the exit. Furthermore, border control has been relocated behind the 25-lane screening platform (Europe's largest) inside the Connector which means that changing planes no longer requires a security check.
Pier B
[edit]Pier B is the oldest pier still in use at Brussels Airport and is only used for flights outside the Schengen Area. Pier B is connected immediately to the main departure hall and consists of two decks. The upper deck (level 3) is at the same level as the departure halls and is used for the departing passengers, whereas the lower deck (level 2) is used for arriving passengers and connects immediately to border control and the baggage claim area.
Planned
[edit]Pier A West
[edit]Pier A West is a planned expansion of Pier A, and is meant to relieve Pier B by also handling flights from non-Schengen countries. Pier A West was due to open in 2016, but because of the slow passenger growth, Brussels Airport announced in July 2013 that the works would be delayed. However, in November 2015, Brussels Airport announced a major 550 million euro investment and pointed out that within this investment the extension of the pier is included.[17]
Low-cost pier
[edit]Just as is the case for Pier A West, the construction of a new low-cost pier is currently on hold. It will be built roughly where the old south pier used to be. At present, several low-cost airlines including Ryanair and Wizz Air fly to Brussels-South Charleroi Airport, 40 km (25 mi) away from Brussels.[18] In autumn 2013, low-cost carrier Pegasus Airlines announced it would end its flights between Brussels Airport and Turkey. The service between Brussels and Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen would relocate to Brussels-South Charleroi Airport. However, Turkish Airlines announced on 26 November 2013 it would offer one daily flight on the same route, starting one month after Pegasus terminated its operations at the airport.[19] One day later, Ryanair announced the opening of a second Belgian base at Brussels Airport, giving a boost to low-cost traffic at Brussels Airport. Ryanair announced on 27 November 10 new routes from Brussels Airport,[20] although Brussels-South Charleroi Airport will remain the low-cost carrier's primary Belgian base.
Services
[edit]Drinking water fountains are found all over the airport. After security check-in, water bottles are available for a small fee.[21]
Shops, bars and restaurants are scattered throughout the building. A few facilities are located in the departure area. These are mostly convenience stores and small shops such as the airport shop, a pharmacy, Relay stores and a coffee shop. But most of the facilities can only be accessed after Security control –and are tax free. Several brands and chains have a branch in both piers, however several only operate in pier A. The airport also features places of worship (for Catholics, Jews, Muslims, Orthodox Christians and Protestants), as well as a place for meditation for humanists.[22] The airport provides meeting facilities and can host congresses up to 600 participants, either in the Regus Skyport Meeting Center or in the Sheraton Brussels Airport Hotel. The latter is the only hotel located on the airport grounds, opposite the terminal. Shuttle services are provided to 14 nearby hotels.
All passengers now have unlimited free Wi-Fi access.[23][24][25]
Other facilities
[edit]Several airlines have or had its head offices at the grounds of Brussels Airport. Brussels Airlines has its corporate head office in the b.house, Airport Building 26, located in Diegem, Machelen.[26][27] European Air Transport had its head office in Building 4–5, in Zaventem.[28] Before Sabena went out of business, its head office was in the Sabena House on the grounds of Brussels Airport.[29] When it existed, Virgin Express had its head office in Building 116 in Zaventem.[30] SN Brussels, which formed in 2002, had its head office in Airport Building 117 in Zaventem when it existed.[31] Prior to its disestablishment, Sobelair had its head office in Building 45 in Zaventem.[32][33] CityBird was based in building 117D.[34] The cargo airline Cargo B Airlines had its head office in the Brucarco Building 706 in Zaventem.[35]
Airlines and destinations
[edit]Passenger
[edit]The following airlines operate regular scheduled and charter flights to and from Brussels:[36]
Cargo
[edit]Statistics
[edit]Traffic
[edit]Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
| Year | Passenger volume | Change over previous year | Aircraft operations | Change over previous year | Cargo (tonnes) | Change over previous year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 22,200,755 | 192,257 | 585,203 | |||
| 2022 | 18,930,698 | 178,930 | 621,482 | |||
| 2021 | 9,357,221 | 118,733 | 668,110 | |||
| 2020 | 6,743,395 | 95,813 | 511,613 | |||
| 2019 | 26,360,003 | 234,460 | 500,702 | |||
| 2018 | 25,675,939 | 235,459 | 543,493 | |||
| 2017 | 24,783,911 | 237,888 | 535,634 | |||
| 2016 | 21,818,418 | 223,688 | 494,637 | |||
| 2015 | 23,460,018 | 239,349 | 489,303 | |||
| 2014 | 21,933,190 | 231,528 | 453,954 | |||
| 2013 | 19,133,222 | 216,678 | 429,938 | |||
| 2012 | 18,971,332 | 223,431 | 459,265 | |||
| 2011 | 18,786,034 | 233,758 | 475,124 | |||
| 2010 | 17,180,606 | 225,682 | 476,135 | |||
| 2009 | 16,999,154 | 231,668 | 449,132 | |||
| 2008 | 18,515,730 | 258,795 | 661,143 | |||
| 2007 | 17,900,000 | 264,366 | 783,727 | |||
| 2006 | 16,707,892 | 254,772 | 719,561 | |||
| 2005 | 16,179,733 | 253,255 | 702,819 | |||
| 2004 | 15,632,773 | 254,070 | 664,375 | |||
| 2003 | 15,194,097 | 252,249 | 607,136 | |||
| 2002 | 14,410,555 | 256,889 | 536,826 | |||
| 2001 | 19,684,867 | 305,532 | 583,729 | |||
| 2000 | 21,637,003 | 352,972 | 687,385 | |||
| 1999 | 20,048,532 | 312,892 | 674,837 | – | ||
| 1998 | 18,400,000 | 300,000 | ||||
| 1997 | 15,900,000 | 277,000 | ||||
| 1996 | 13,400,000 | 264,000 | – | |||
| 1995 | 12,500,000 | |||||
| 1994 | 11,200,000 | – | ||||
| 1993 | 10,000,000+ | – | ||||
| 1950 | 240,000+ | – |
- The relapse in 2001 and 2002 is due to the combined effects of the September 11 attacks and the collapse of then home carrier Sabena in the final quarter of 2001.
- The cargo relapse in 2008 and 2009 is due to the combined effects of the Financial crisis of 2007–08, also affecting passenger volumes in 2009, and the relocation of DHL Aviation to Leipzig/Halle Airport. DHL departed after the Belgian government decided they could not operate more cargo flights at night because of noise for the people living in the surrounding area.
- The 2016 decrease in passenger numbers and aircraft movements results from the 2016 Brussels bombings which caused the airport to close for 11 days before reopening with severely reduced capacity.
Routes
[edit]| Rank | Destination | Airport(s) | Passengers 2018 | Passengers 2017 | Passengers 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Madrid | MAD | 1,009,602 | 966,146 | 763,016 |
| 2 | Barcelona | BCN | 940,782 | 927,618 | 889,180 |
| 3 | Lisbon | LIS | 733,920 | 738,243 | 698,131 |
| 4 | Rome | FCO | 720,067 | 719,436 | 713,392 |
| 5 | London | LHR | 688,333 | 654,712 | 587,487 |
| 6 | Milan | MXP, LIN | 639,346 | 644,841 | 492,068 |
| 7 | Geneva | GVA | 608,377 | 591,857 | 545,230 |
| 8 | Frankfurt | FRA | 589,109 | 549,296 | 467,068 |
| 9 | Málaga | AGP | 537,230 | 533,863 | 499,228 |
| 10 | Berlin | TXL, SXF | 497,362 | 622,816 | 703,272 |
| Rank | Destination | Airport(s) | Passengers 2018 | Passengers 2017 | Passengers 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New York City | JFK, EWR | 472,960 | 454,187 | 441,212 |
| 2 | Dubai | DXB | 343,452 | 228,001 | 187,049 |
| 3 | Tel Aviv | TLV | 287,627 | 295,464 | 267,366 |
| 4 | Washington, D.C. | IAD | 251,655 | 231,859 | 212,027 |
| 5 | Montréal | YUL | 205,282 | 197,550 | 174,843 |
| 6 | Doha | DOH | 172,493 | 169,111 | 156,644 |
| 7 | Abu Dhabi | AUH | 154,054 | 170,549 | 144,239 |
| 8 | Casablanca | CMN | 145,218 | 159,188 | 142,294 |
| 9 | Bangkok | BKK | 142,175 | 125,264 | N/A |
| 10 | Chicago | ORD | 139,487 | 131,388 | 92,282 |
Ground transportation
[edit]Road
[edit]
Brussels Airport can be reached by car via the A201, which is directly connected to the Brussels Ring Road. From there, the main highways of Belgium can directly be accessed. Private partners provide three car parks at the airport, offering in total 10,600 parking spaces. Shell operates a self-service gas station near the exit of the airport complex.
Several car rental services are located in the airport as well. Europcar, Hertz, Sixt and Thrifty all operate at Brussels Airport. DriveNow also offers a car-sharing service at Brussels airport located at P3 Holiday Parking,[150] and Zipcar has parking spaces.[151] Taxi2Share provides sharing cab service from airport.
De Lijn provides bus transportation to and from various cities in Flanders from platforms A and B (via Brucargo). The MIVB/STIB provides transportation into Brussels city centre from Schuman railway station, Brussels Luxembourg Station and Trône Metro Station via line 12 from platform C. Platform E is used by the Hotel Shuttles, offering shuttle services to several hotels near the area.
Taxis are permanently available in front of the arrivals hall. Licensed taxis can be recognized by the blue and yellow emblem.
Rail
[edit]
The Airport Railway Station is located under the airport building at level −1. The train station has direct services to Antwerp, Brussels, De Panne, Ghent, Hasselt, Landen, Leuven, Mechelen, Nivelles and Quévy. At least four trains per hour serve the most used link to Brussels South Railway Station, where international connections are offered by Eurostar (to Amsterdam, Avignon, Cologne, Essen, Lille, London, Marseille, Paris and Valence), ICE (to Cologne and Frankfurt), and Eurocity (to Basel, Bern, Chur, Luxembourg and Zürich).
A direct train link with Leuven was opened on 12 December 2005. A direct link with Antwerp and Mechelen via the so-called Diabolo line was opened for public service on 10 June 2012. The Diabolo project is a public-private partnership. It has been decided that all rail passengers to the Brussels Airport-Zaventem railway station pay a "Diabolo supplement" to finance the ongoing and planned work.
As of December 2014, a direct train link between Bruges and the Airport will be offered,[152] just as an Intercity service to Schiphol and Amsterdam.[153]
Since the new Schuman-Josaphat tunnel[154] has been finished, a new connection has been established to connect Brussels Airport directly to the stations of the EU quarter, being Brussels-Schuman and Brussels-Luxembourg. This brought the travel time between the Airport and the EU quarter to 15 minutes. The Belgian Railways announced the line to open as an hourly service.[155][156][157] However, the line now sees a train every 30 minutes on weekdays.[158]
Tram
[edit]In an attempt to alleviate gridlock around Brussels, the Flemish regional transport company De Lijn started the Brabantnet project, which was then scheduled to be finished by 2020.[159] Three new light rail lines will be created, of which 2 will terminate at Brussels Airport:
- The Airport Tram, connecting Brussels Airport to Brussels-North, but taking a different trajectory from the existing railway line;
- The Ring Tram, roughly following the northern side of the Brussels Ring and connecting several Brussels suburbs and Vilvoorde to the Airport.
To speed up the process, testing started in August 2016 with a Trambus, a Bus rapid transit system developed by Belgian bus builder Van Hool, which requires less investment than a tram.[160] The Ringtrambus started service on 28 July 2020, using 14 24-metre double-articulated buses. The initial half-hourly service is to be upgraded to quarter-hourly on 1 September 2020.[161] Route 820 runs between Brussels Airport and the Brussels University Hospital in Jette, via Brucargo, the station and the centre of Vilvoorde, the Kassei neighbourhood, the employment area around the Medialaan, Strombeek and the Heysel. This solution is presented as an in-between step until the tram line is finished.[162]
The Airport Tram will be an extension of present Brussels Tram line 55 and line 62,[163] and will roughly follow the A201 Motorway, but will need a large bridge to cross the Brussels Ring into the Airport.[164] The present trams' tracks end at the Eurocontrol headquarters, but the extension will lead from the Bourget roundabout along the A12 into the Airport. The new line will be a so-called 'high frequency' line (comparable to Brussels tram route 7 and 8) connecting the northern part of the city with the Business zone next to the airport and the Airport itself.[165]
Bicycle
[edit]Brussels Airport has a special separated road that provides access to the airport for bikers and pedestrians. There is also a special place to park bikes. Since 2019, the airport has a direct connection from the bicycle freeway Brussels – Leuven ("Fietssnelweg F3").[166] In 2016, merely 1% of employees were commuting by bike.[167] In an effort to further increase this number, bicycle leasing was introduced to employees, and in 2020 almost 10% of the Brussels Airport employees signed up for this.[168]
Accidents and incidents
[edit]
- On 17 September 1946, a Sabena Douglas DC-3 went into a half roll and crashed into some hangars on takeoff because of loss of airspeed. One crewmember out of the seven occupants on board was killed.[169]
- On 15 February 1961, Sabena Flight 548, a Boeing 707, crashed during approach on runway 20, killing all 72 people on board and one on the ground.[170] This was the first fatal accident involving a Boeing 707, resulting in the death of the entire United States Figure Skating team on its way to the World Figure Skating Championships in Prague, Czechoslovakia, which the International Skating Union subsequently cancelled out of respect for the team.
- On 25 May 2008, Kalitta Air Flight 207, a Boeing 747-200F, overran the shorter runway 20, crashed into a field and split in three. Four of the five people on board received minor injuries.[171]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
- ^ a b "Brussels Airport Traffic December 2016". Brussels Airport. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
- ^ a b EBBR – BRUSSELS / Brussels-National (also PDF). Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP) from AIM Belgium via skeyes.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Facts and Figures-Airport Infrastructure". brusselsairport.be. Retrieved 5 October 2023.
- ^ "Moody's assigns (P)Baa1 rating to Brussels Airport Holding SA/NV's senior secured debt; stable outlook". Moodys.com. 13 June 2013. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ a b John Martens (3 April 2016). "Brussels Reconnects With NYC, Africa as Airport Shifts Gear". Bloomberg.com.
- ^ "Record day at Brussels Airport with 90,000 passengers expected". Archived from the original on 2 August 2016. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- ^ Robert Tom. "Brussels Explosion rocks Europe!". Innovative Report. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 22 March 2016.
- ^ "Zaventem airport". Atob. 19 August 2022.
- ^ Expatica: Record numbers of passengers at Brussels Airport Archived 9 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Brussels Airport vervangt borden met vluchtinformatie". HLN. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011.
- ^ Higgins, Andrew (18 February 2013). "Brazen Jewel Robbery at Brussels Airport Nets $50 Million in Diamonds". The New York Times. Retrieved 20 February 2013.
- ^ Casert, Raf (19 February 2013). "Casert, Raf, "Robbers Snatch $50 Million of Diamonds Off Plane in Belgium," Associated Press, February 19, 2013, 4:13 a.m". Worldnews.nbcnews.com. Archived from the original on 21 February 2013.
- ^ Casert, Raf (19 February 2013). "Smith, Vicky, "The Great Plane Robbery: Gang of Fake Police Officers Steal £32m of Diamonds in Airport Heist," Associated Press, February 19, 2013, 18:49". Worldnews.nbcnews.com. Archived from the original on 21 February 2013.
- ^ Lizzie Dearden (22 March 2016). "Isis claims responsibility for Brussels attacks". The Independent.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Plattegrond terminal". Archived from the original on 3 December 2013.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Introduction". Archived from the original on 29 January 2017. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Brussels Airport lowers airport tariffs by 5.2% and invests over €550 million in its infrastructure". Archived from the original on 21 December 2015.
- ^ "Shuttles Brussels – Charleroi Airport". Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Turkish Airlines Adds Istanbul Sabiha Gokcen – Brussels / Berlin in S14". Routes. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Welcome to Ryanair!". Ryanair.com.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Drinking water, Brussels Airport
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Praying and mediation", Brussels Airport
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Unlimited free Wi-Fi". www.brusselsairport.be. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2016.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: Internet & Telephony". Archived from the original on 29 January 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2015.
- ^ "Brussels Airport on Twitter". Twitter. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- ^ ""Bedrijf". Machelen Diegem. Archived from the original on 24 May 2010.
- ^ "Contact us". Brussels Airlines. Archived from the original on 13 October 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2009.
- ^ "General Conditions of Carriage". DHL. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Von Schreiber, Sylvia (26 November 2001). "Organisierte Pleite". Der Spiegel. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015.
- ^ "World Airline Directory." Flight Global. 30 March – 5 April 2004. 92.
- ^ "World Airline Directory." Flight International. 30 March – 5 April 2004. 71.
- ^ "Survey: World Airlines." Flight International. 1–7 April 2003. 74.
- ^ "Contact Us." Sobelair. 5 December 2002. Retrieved on 27 May 2010.
- ^ "City Bird: Contact us". 3 November 1999. Archived from the original on 3 November 1999.
- ^ Welcome, 18 April 2008. Retrieved on 20 February 2012.
- ^ "Discover over 200 destinations | Brussels Airport". Brussels Airport Website. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Air Arabia Maroc launches flights from new base Rabat to five European destinations, including Brussels". Aeroroutes. 12 February 2024. Retrieved 13 February 2024.
- ^ "Air Arabia Maroc Launches Tetouan – Europe Service in NS24". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 15 January 2024.
- ^ "airBaltic launches flights from Brussels to Tallinn in Summer 2019 – Aviation24.be". 16 August 2018.
- ^ "Air Canada to fly between Toronto and Brussels". Aviacionline. 30 July 2022. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- ^ "Air Canada Moves Toronto – Brussels Launch to August 2023". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ^ https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240229-juns24freq
- ^ "Air Transat in 2021 weer naar Schiphol en Brussels Airport". 29 October 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ^ Liu, Jim. "Turkish Airlines confirms AnadoluJet network transition from late-March 2020". Routesonline. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ "News for Airlines, Airports and the Aviation Industry | CAPA".
- ^ "ANA NW23 European Operations – 15SEP23".
- ^ "Summer season Brussels Airport 2024".
- ^ "Austrian Airlines NW25 Systemwide Flight Number Changes – 30OCT24". Aeroroutes. Aeroroutes. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- ^ "Austrian Expands Innsbruck Network in NW24". AeroRoutes. 3 July 2024. Retrieved 3 July 2024.
- ^ "British Airways NW24 Heathrow – Europe Frequency Changes – 27OCT24". Aeroroutes. Aeroroutes. Retrieved 31 October 2024.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines". brusselsairlines.com.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Brussels Airlines NW24 West/Central Africa Network Adjustment – 08SEP24". Aeroroutes.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y "Brussels Airlines NW24 Europe Frequency Changes – 26MAY24". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines increases capacity by Summer 2023, signs wet-lease agreement with CityJet and hires new staff". 7 December 2022.
- ^ a b "Brussels Airlines NW23 Intercontinental Network Overview – 11OCT23". Aeroroutes.
- ^ a b "Brussels Airlines vaker naar Afrika en VS dankzij extra Airbus A330". 14 December 2021.
- ^ a b c "Lufthansa Group Carriers July/August 2022 Intra-Europe Adjustment - 26JUN22". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines reopens attractive holiday destinations and launches Brussels-Frankfurt". 24 February 2021.
- ^ "Thomas Cook / Brussels Airlines partnership gives Belgian holidaymakers more choice, more flexibility and more certainty as from 28 October". aviation.be. 20 September 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Brussels Airlines NS23 European Network Adjustment – 18DEC22". Aeroroutes.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Brussels Airlines boosts summer services with expanded fleet and premium offerings". 24 June 2024.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines NW24 Nairobi Operations – 18APR24". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "Pasazer.com: Brussels Airlines wraca do Krakowa". Pasazer.com. 17 October 2023.
- ^ a b Liu, Jim. "brussels airlines resumes Luanda / New York service in Feb 2021". Routesonline. Retrieved 2 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Brussels Airlines adds eight new destinations to its Summer 2022 schedule". 18 January 2022.
- ^ "Lufthansa Group Carriers NS24 Intercontinental Network Adjustment – 13SEP23". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines NW24 Europe Frequency Changes – 27OCT24". Aeroroutes. Aeroroutes. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- ^ "Brussels airlines trades Bromma for Arlanda". 16 June 2023.
- ^ "Belgium's Brussels Airlines to restart flights to Israel". The Jerusalem Post. 22 February 2024. Retrieved 22 February 2024.
- ^ a b "Brussels Airlines launches its holiday offer for summer 2021". press.brusselsairlines.com. 26 December 2020.
- ^ "In the next two years, Brussels Airlines will add five Airbus A320neo to the fleet". 7 December 2022.
- ^ a b c "Brussels Airlines NS23 Short-Haul Network Additions". AeroRoutes.
- ^ "Shrinking not sprouting – Brussels struggles on some UK short haul routes post-Brexit". 22 February 2024. Retrieved 22 February 2024.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines Adds Brindisi Service in NS23". Aeroroutes. 22 November 2022. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines launches its holiday offer for summer 2022". 6 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Brussels Airlines lanceert nieuwe routes en richt zich sterk op vakantie- en VFR-markt". 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines Schedules Seasonal Morocco Service in NS22". AeroRoutes.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines Adds Sharm El Sheikh Service in NW23". AeroRoutes. 27 June 2023. Retrieved 27 June 2023.
- ^ "Brussels Airlines Grows Again". 28 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "Forfaits voyage : Brussels Airlines signe avec NORDIC et Sunweb | Air Journal". 31 March 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g Orban, André (14 March 2022). "Corendon significantly expands its offer on the Belgian market: 22 destinations from Brussels, 9 from Maastricht".
- ^ "Corendon Airlines NW22 Scheduled Service Adjustment – 20OCT22". aeroroutes.com. 20 October 2022.
- ^ "Cyprus Airways launches flights between Larnaca and Brussels from February 2024". 5 December 2023.
- ^ "Dan Air: 13 rute de la Bacău cu debut în noiembrie și decembrie 2023". November 2023.
- ^ "Delta Expands in Europe with First-Ever Nonstop Flights to Catania". Business Traveler. 20 September 2024. Retrieved 20 September 2024.
- ^ "Delta NW24 intercontinental network changes". aeroroutes.com. 27 April 2024.
- ^ "Finnair August 2022 European Network Adjustment - 24JUL22". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "flynas schedules Berlin/Brussels flights". 9 October 2023.
- ^ "FLYONE va opera șapte rute noi din Chișinău în vara anului 2022". 15 December 2021.
- ^ "Direct flights from Brussels (BRU) - FlightConnections". 16 July 2023.
- ^ "Welcome on Hainan Airlines website !". www.hainanairlines.com.
- ^ "Hainan Airlines Resumes Shanghai – Brussels From June 2024". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ "Mainland Chinese Carriers NS23 International/Regional Network - 14MAY23". AeroRoutes. 15 May 2023. Retrieved 15 May 2023.
- ^ "HiSky: București - Bruxelles BRU din noiembrie 2022". 8 September 2022.
- ^ "IBERIA NW24 Madrid – Europe Frequency Changes – 26MAY24". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "Alitalia to stop operations in October". travelweekly.co.uk. 26 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ "Juneyao Airlines Plans Brussels / Manchester July 2024 Launch".
- ^ "KLM NS24 European Service Changes – 21JAN24". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "New airline replacing Air Malta to fly on March 31, 2024". 2 October 2023.
- ^ "Direkte fra Tromsø til Brüssel og Stockholm". Dfly.no. Retrieved 5 June 2024.
- ^ Liu, Jim. "Nouvelair Tunisie plans Djerba – Brussels service from late-Oct 2020". Routesonline. Retrieved 25 August 2020.
- ^ Liu, Jim (22 October 2019). "Nouvelair Tunisie schedules new regular routes in S20". routesonline.com.
- ^ "Play Airlines behalve naar Schiphol ook naar Brussel" [Play Airlines announces flights to Brussels, Schiphol]. Luchtvaartnieuws (in Dutch). 2 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "Brussels Airport presents Summer 2022 schedule; 6 new destinations and 4 new airlines". 17 March 2022.
- ^ "Royal Jordanian Plans Brussels Service Resumption in NW23".
- ^ "Royal Jordanian gaat weer op Brussel vliegen". 24 March 2023.
- ^ "Ryanair NS23 Porto Frequency Variations – 19FEB23". Aeroroutes.
- ^ "Introducing Brussels - Singapore – Fly non-stop from Brussels to Singapore and beyond from 6 April 2024". Singapore Airlines. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ^ a b "Flight Tickets". www.skyexpress.gr.
- ^ Liu, Jim. "SunExpress S20 network additions as of 22OCT19". Routesonline. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- ^ "10 Ağustos'ta Adana Şakirpaşa Havalimanı kapatılıyor! Uçuşlar yeni havalimanına aktarılacak".
- ^ "Book cheap flights & fly to top destinations | sunexpress.com". SunExpress EN. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "SWISS vliegt vanaf 27 maart tussen Genève en Brussel". 14 December 2021.
- ^ "SWISS NW24 Europe Frequency Changes – 27OCT24". Aeroroutes. Aeroroutes. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- ^ "THAI keert terug naar Brussel met dagelijkse vlucht". 31 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d "Transavia breidt aantal zomerbestemmingen op Brussels Airport uit". 8 March 2023.
- ^ "Transavia apre Bari-Bruxelles nel 2024". 20 September 2023.
- ^ "Transavia NS24 Network Additions – 24SEP23".
- ^ "Transavia France NS25 Network Additions – 22OCT24". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 23 October 2024.
- ^ "Transavia to Launch Thessaloniki-Brussels Route in Summer 2024". 21 September 2023.
- ^ a b "Transavia vliegt komende zomer vanaf Brussels airport". 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Summer 2023: Transavia is expanding in Brussels". 10 March 2023.
- ^ "Transavia: Nieuwe bestemmingen vanaf Brussels Airport". 21 December 2022.
- ^ "Flight plan". tuifly.be. Archived from the original on 22 October 2016. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f "TUIfly Belgium 2023 North Africa Network Additions". AeroRoutes.
- ^ "TUIfly Belgium NS23 Morocco Network Additions".
- ^ "TUIfly Belgium Adds Curacao From Nov 2024". Aeroroutes. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "Dakar, Senegal, new TUIfly Belgium destination from 4 July". 18 March 2022.
- ^ "AeroRoutes".[permanent dead link]
- ^ https://www.aeroroutes.com/eng/240829-tbaug24rmu
- ^ "Vueling start lijndienst van Brussel naar Sevilla". 3 March 2023.
- ^ "New route from Brussels to the Norwegian fjords". 15 November 2023.
- ^ "BREAKING: Hungarian Wizz Air launches six new flights from Budapest! - UPDATED - Daily News Hungary". 28 February 2024.
- ^ "Egyptair Cargo 1Q24 Belgium Service Changes". AeroRoutes.
- ^ skychain.emirates.com - View Schedule [permanent dead link] retrieved 24 July 2020
- ^ "Route Network (June 2024)". Emirates SkyCargo. June 2024. Retrieved 22 June 2024.
- ^ cargo.ethiopianairlines.com - Route Map retrieved 24 July 2020
- ^ latamcargo.com - Route offering retrieved 24 July 2020
- ^ qrcargo.com retrieved 12 September 2019
- ^ cargo.royalairmaroc.com - Our destinations retrieved 24 July 2020
- ^ siacargo.com - Flight Schedule retrieved 24 July 2020
- ^ "Suparna Airlines start cargovluchten naar Brussels Airport". Flightlevel. 2 April 2020.
- ^ turkishcargo.com - Flight Schedule retrieved 4 July 2020
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 26 March 2017. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Monthly traffic figures | Brussels Airport". Brussels Airport Website. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "22.2 million passengers at Brussels Airport in 2023, up 17% on 2022 - 701,000 tonnes of cargo transported through the airport". Brussels Airport. 12 January 2024. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b "Brutrends 2018". issuu. 9 July 2019. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 May 2018. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Car Sharing Brussels Airport – Parking & Prices – DriveNow". www.drive-now.com.
- ^ "can I park a zipcar at the airport? - Zipcar". www.zipcar.be. Archived from the original on 18 March 2018. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "Meeting Spotlight Homepage | Meeting Spotlight". www.meetingspotlight.com. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ SNCB International. "Hop on and head for the Netherlands". Archived from the original on 31 January 2017. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ "Brochure Schuman-Josafat (2008)". Archived from the original on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ "The Regional Express Network". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ "Horaierees December 2015". Archived from the original on 18 September 2015. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "De erg bescheiden start van stations Mouterij en Thurn & Taxis | Brusselnieuws" (in Dutch). Brusselnieuws.be. Retrieved 18 December 2015.
- ^ "NMBS/SNCB – Timetable & buy tickets".
- ^ "Brabantnet". Archived from the original on 17 October 2017. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ "First trambus in Belgium makes maiden trip". www.brusselsairport.be.
- ^ [1] [permanent dead link]
- ^ "'Trambus vanaf 2019 in Noordrand'". De Standaard. 21 August 2016. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Brussel en Vlaanderen akkoord over luchthaventram". bruzz.be. Bruzz.
- ^ "Brussel-Noord – Brussels Airport". delijn.be.
- ^ "Vergunning afgeleverd voor deel van tramlijn naar luchthaven".
- ^ "Bicycle or motorcycle | Brussels Airport". Brussels Airport Website. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ "Brussels Airport Website: New fast cycle route to Brussels Airport". Archived from the original on 14 March 2016.
- ^ "Bicycle leasing for Brussels Airport employees: to the airport by bike (accessed March 23, 2020)". 27 February 2020.
- ^ Accident description for OO-AUR at the Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved on October 5, 2023.
- ^ "AirDisaster.Com". AirDisaster.Com. 15 February 1961. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "Plane comes off Brussels runway". BBC News. 25 May 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2009.
Notes
[edit]External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Brussels Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Brussels Airport at Wikimedia Commons
- Official website (in English)
- Current weather for EBBR at NOAA/NWS
- Accident history for BRU at Aviation Safety Network



